The Internet of Things is not just a concept; it is the foundational fabric of tomorrow’s digital world.”
— Satya Nadella, CEO of Microsoft
The Internet of Things (IoT) has emerged as one of the most transformative technologies of our time, reshaping industries, improving lives, and driving innovation. From wearables that monitor health metrics to industrial systems that predict machine failures, IoT connects billions of devices to create smarter, data-driven ecosystems. But what exactly is IoT, and why is it so important? This detailed guide explores the essential aspects of IoT and its profound impact on our world.
What Does IoT Stand For?
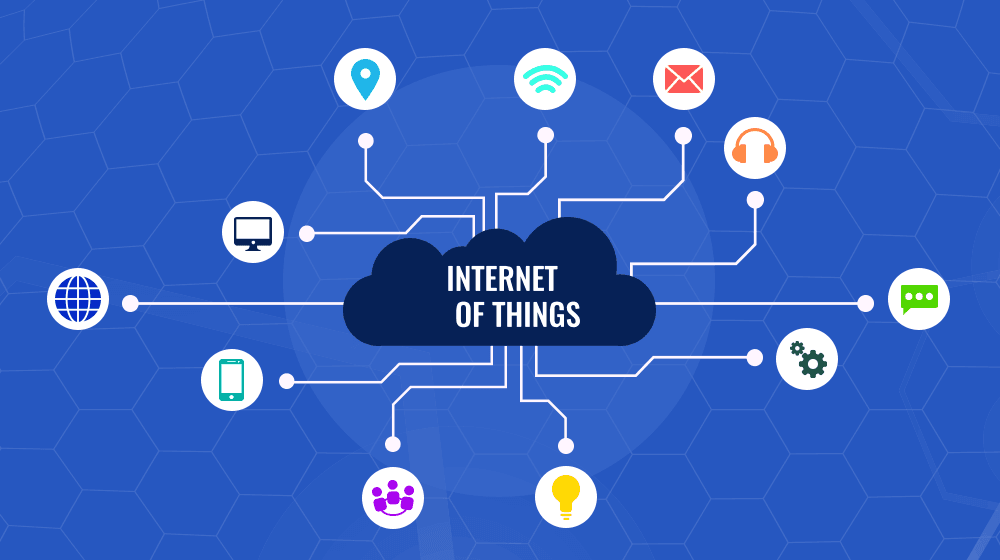
IoT stands for Internet of Things, a term that describes a vast network of physical objects—devices, appliances, vehicles, and even buildings—that are equipped with sensors, software, and connectivity to exchange data over the internet.
This concept has redefined the way devices interact. IoT isn’t limited to high-tech gadgets; it encompasses everyday items like thermostats, refrigerators, and light bulbs. These devices collect data, process it, and often act autonomously, transforming static objects into intelligent tools that enhance efficiency, safety, and convenience.

What is the Internet of Things (IoT)?
The Internet of Things represents the integration of digital and physical worlds, where devices communicate with each other and with humans to provide valuable insights or automate processes. This interconnected ecosystem includes everything from smart home gadgets to industrial robots and healthcare monitors.
For example, in agriculture, IoT-enabled drones monitor crop health, while soil sensors optimize irrigation and fertilizer use. In cities, IoT powers smart traffic lights and parking systems, reducing congestion and energy waste. By 2023, IoT was instrumental in areas like telemedicine, enabling doctors to remotely monitor patients’ vital signs through wearable devices.
IoT is not just about connecting devices; it’s about creating systems that think, learn, and adapt—delivering efficiency, innovation, and sustainability.
How Does IoT Work?
IoT operates through a seamless combination of hardware, software, and connectivity, driven by the following four components:
1. Sensors and Devices:
Sensors are the heart of IoT systems. These components collect real-time data, such as temperature, pressure, movement, or sound, from their surroundings. A smartwatch, for instance, measures heart rate and step count, while a factory sensor tracks vibration levels to predict machinery malfunctions.
2. Connectivity:
Data from sensors is transmitted to a central system or cloud platform through networks like Wi-Fi, cellular networks (4G/5G), Bluetooth, Zigbee, or LPWAN (Low Power Wide Area Network). IoT-specific technologies such as LoRaWAN have gained popularity for their ability to connect devices over long distances with minimal energy consumption.
3. Data Processing and Analytics:
Once data is transmitted, cloud-based systems or edge computing platforms analyze it to derive insights or trigger actions. For example, a smart refrigerator might analyze inventory levels and automatically order groceries when supplies run low. Artificial intelligence (AI) plays a significant role here, enabling devices to learn user behavior and optimize performance over time.
4. User Interface (UI):
The final layer is the user interface, which allows people to interact with IoT devices. Whether through smartphone apps, voice commands, or web dashboards, the UI provides control and visibility into the device’s functions. For instance, homeowners can use an app to monitor security cameras or adjust lighting remotely.

Why Does IoT Matter?
The Internet of Things is reshaping industries and improving everyday life by enabling better decision-making, optimizing operations, and enhancing convenience. With over 15 billion IoT devices in use by 2023, and predictions exceeding 75 billion by 2025, its significance cannot be overstated.
Key Impacts of IoT:
- Efficiency Improvements: IoT devices automate mundane tasks, from turning off lights to optimizing energy use in factories, saving time and resources.
- Data-Driven Decisions: By analyzing data from IoT systems, businesses and governments can make informed decisions to improve productivity, safety, and sustainability.
- Innovation and Growth: IoT is a driver of innovation, leading to new products, services, and business models, such as telemedicine, autonomous vehicles, and predictive maintenance.
IoT’s ability to bridge the digital and physical realms makes it a cornerstone of the modern digital ecosystem.

Fun Facts About IoT
The evolution of IoT is marked by staggering growth and technological advancements:
- Market Expansion: The IoT market grew from $2.99 trillion in 2014 to $15 trillion by 2023, driven by advancements in 5G, AI, and cloud computing.
- Connected Devices: By 2025, over 75 billion IoT devices will be operational, up from 15 billion in 2023.
- Economic Impact: IoT could generate a global economic impact of $11.1 trillion annually by 2025, transforming industries such as manufacturing, transportation, and healthcare.
IoT’s rapid evolution highlights its pivotal role in shaping the future of technology.
Benefits of the Internet of Things
1. Revolutionizing Industrial Automation
IoT enables industries to streamline operations through predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring. In manufacturing, sensors on equipment predict failures, allowing maintenance teams to address issues before breakdowns occur, minimizing downtime and costs.
2. Transforming Data Collection and Utilization
IoT generates massive amounts of data, enabling businesses to gain insights into customer behavior, optimize supply chains, and improve product performance. For example, logistics companies use IoT to track shipments in real time, ensuring timely deliveries.
3. Enhancing Customer Experience
IoT allows businesses to deliver hyper-personalized experiences. For instance, smart thermostats learn user preferences to maintain ideal home temperatures, while fitness apps offer tailored recommendations based on individual activity levels.
4. Driving Cost Savings and Revenue Growth
IoT reduces overhead costs by optimizing resource utilization and preventing waste. Retailers use IoT-powered inventory systems to track stock levels and prevent overstocking or shortages, boosting profitability.
Challenges of IoT
While IoT presents immense opportunities, it also comes with challenges:
1. Cybersecurity Risks:
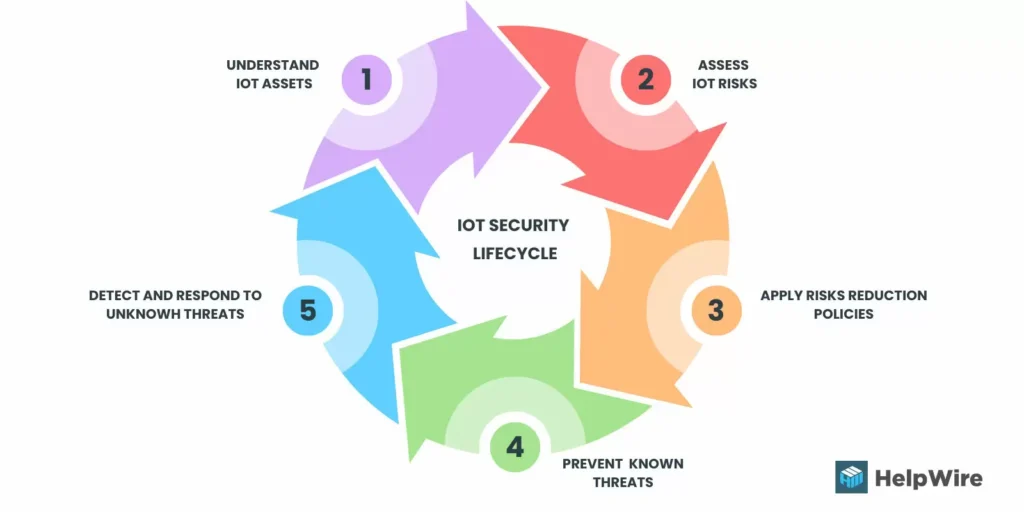
Cybersecurity Risks: The growing number of connected devices increases vulnerability to cyberattacks. Hackers could exploit IoT systems to access sensitive data or disrupt critical operations. Strengthening encryption, implementing secure authentication methods, and adhering to best practices are essential to mitigate risks. Learn 25 tips to strengthen your API security in minutes to ensure that your IoT systems are secure from potential vulnerabilities.
2. Lack of Standardization:
The absence of universal standards for IoT devices hampers interoperability and integration. Industry-wide collaboration is necessary to establish protocols that ensure seamless communication and enhanced security.
Leading IoT Companies and Platforms
Several companies are at the forefront of IoT innovation:
- Amazon AWS IoT: Offers a comprehensive platform for building and deploying IoT solutions.
- Google Cloud IoT: Provides tools for managing connected devices and processing IoT data.
- Microsoft Azure IoT Hub: Enables seamless integration of IoT devices with cloud services.
- Qualcomm: Develops advanced processors and communication technologies for IoT devices.
The Future of IoT
The future of IoT is poised to revolutionize industries further with advancements in edge computing, 5G, and artificial intelligence. Emerging trends include:
- Smart Cities: IoT will power intelligent infrastructure, reducing energy consumption, managing traffic, and enhancing public safety.
- Healthcare Innovations: IoT-enabled wearables will provide real-time health monitoring, improving patient outcomes.
- Industrial IoT (IIoT): Factories will leverage IoT for precision manufacturing, predictive analytics, and energy optimization.
Despite these advancements, addressing IoT’s security and integration challenges will remain critical for its widespread adoption.

Why IoT Requires Integration
IoT’s success hinges on the ability to integrate devices, data, and systems seamlessly. A McKinsey study revealed that over 99% of data generated by IoT sensors in industries like oil and gas was not utilized, highlighting the need for effective integration solutions.
Businesses must invest in scalable infrastructures that support data aggregation, hybrid cloud systems, and secure data transfer to unlock IoT’s full potential.
Conclusion
The Internet of Things is not just a technological advancement; it’s a revolution transforming industries, enhancing lives, and shaping the future. With endless applications, IoT’s impact will only grow in the coming years.
MyceliumWeb is a leading provider of innovative digital solutions, specializing in IoT integration, data-driven strategies, and technology consulting. We help businesses harness the power of connected devices to optimize operations, enhance customer experiences, and drive growth. Whether you’re starting your IoT journey or seeking to scale, MyceliumWeb delivers customized, future-ready solutions tailored to your needs.